Description
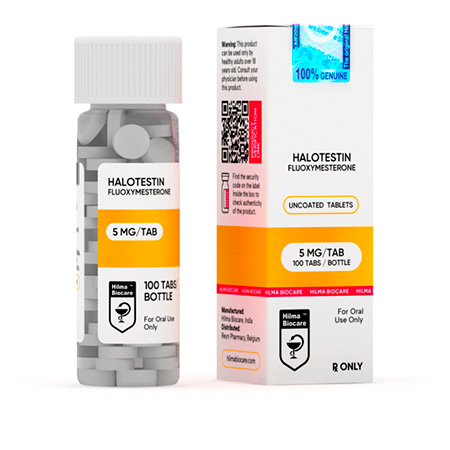
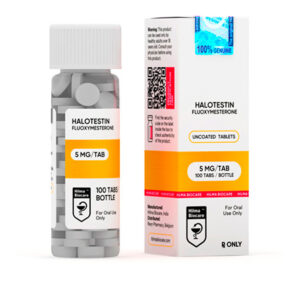
Halotestin
Strength: 5 mg
Molecular Formula: C21H32O3
Molecular Weight: 336,45 g/mol
Active Ingredient: Fluoxymesterone
CAS number: 76-43-7
Dosage Form: Tablet
Route: Oral
Market Status: Prescription
Company: Hilma Biocare
DESCRIPTION
Fluoxymesterone is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the
treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, breast cancer in
women, and anemia.
INDICATIONS
In the male fluoxymesterone is indicated for: – Replacement therapy in conditions associated
with symptoms of deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone. – Primary
hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) – testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral
torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome; or orchidectomy. – Hypogonadotropic
hypogonadism (congenital or acquired)-idiopathic gonadotropin or LHRH deficiency, or
pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. Delayed puberty, provided it
has been definitely established as such, and is not just a familial trait. In the female
fluoxymesterone is indicated for palliation of androgen- responsive recurrent mammary
cancer in women who are more than one year but less than five years postmenopausal.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to the drug – Males with carcinoma of the breast – Males with known
or suspected carcinoma of the prostate gland – Women known or suspected to be pregnant –
Patients with serious cardiac, hepatic or renal disease.
SIDE EFFECTS
Endocrine and urogenital Female: the most common side effects of androgen therapy are
amenorrhea and other menstrual irregularities; inhibition of gonadotropin secretion; and
virilization, including deepening of the voice and clitoral enlargement. The latter usually is not
reversible after androgens are discontinued. When administered to a pregnant woman,
androgens can cause virilization of external genitalia of the female fetus. Male:
Gynecomastia, and excessive frequency and duration of penile erections. Oligospermia may
occur at high dosage.
Skin and appendages Hirsutism, male pattern of baldness, seborrhea, and acne.
Fluid and electrolyte disturbances, retention of sodium, chloride, water, potassium, calcium,
and inorganic phosphates.
Gastrointestinal Nausea, cholestatic jaundice, alterations in liver function tests, rarely
hepatocellular neoplasms and peliosis hepatis.
Hematologic Suppression of clotting factors II, V, VII, and X, bleeding in patients on
concomitant anticoagulant therapy, and polycythemia.
Nervous system Increased or decreased libido, headache, anxiety, depression, and
generalized paresthesia.
PRECAUTIONS
Women should be observed for signs of virilization which is usual following androgen use at
high doses. Discontinuation of drug therapy at the time of evidence of mild virilism is
necessary to prevent irreversible virilization. A decision may be made by the patient and the
physician that some virilization will be tolerated during treatment for breast carcinoma.
Patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy may develop acute urethral obstruction. Priapism
or excessive sexual stimulation may develop. Oligospermia may occur after prolonged
administration or excessive dosage. If any of these effects appear, the androgen should be
stopped and if restarted, a lower dosage should be used. This product contains tartrazine
which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible
individuals. Although the overall incidence of tartrazine sensitivity in the general population is
low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have an aspirin hypersensitivity. Because of
the hepatotoxicity associated with the use of 17-alpha- alkylated androgens, liver function
tests should be obtained periodically. Periodic (every six months) X-ray examinations of
bone age should be made during treatment of prepubertal males to determine the rate of
bone maturation and the effects of androgen therapy on the epiphyseal centers. Serum
cholesterol may increase during androgen therapy. There are rare reports of hepatocellular
carcinoma in patients receiving long-term therapy with androgens in high doses. Withdrawal
of the drugs did not lead to regression of the tumors in all cases. Geriatric patients treated
with androgens may be at an increased risk of developing prostatic hypertrophy and
prostatic carcinoma although conclusive evidence to support this concept is lacking.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Androgens may increase sensitivity to oral anticoagulants. Dosage of the anticoagulant may
require reduction in order to maintain satisfactory therapeutic hypoprothrombinemia.
Concurrent administration of oxyphenbutazone and androgens may result in elevated serum
levels of oxyphenbutazone. In diabetic patients, the metabolic effects of androgens may
decrease blood glucose and, therefore, insulin requirements. Androgens may decrease
levels of thyroxine-binding globulin, resulting in decreased total T4 serum levels and
increased resin uptake of T3 and T4. Free thyroid hormone levels remain unchanged,
however, there is no clinical evidence of thyroid dysfunction.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dosage will vary depending upon the individual, the condition being treated, and its
seventy. The total daily oral dose may be administered singly or in divided (three or four)
doses. Male hypogonadism: For complete replacement in the hypogonadal male, a daily
dose of 5 to 20 mg will suffice in the majority of patients. It is usually preferable to begin
treatment with full therapeutic doses which are later adjusted to individual requirements.
Priapism is indicative of excessive dosage and is an indication for temporary withdrawal of
the drug. Delayed puberty: Dosage should be. carefully titrated utilizing a low dose,
appropriate skeletal monitoring, and by limiting the duration of therapy to four to six months.
Inoperable carcinoma of the breast in the female: The recommended total daily dose for
palliative therapy in advanced inoperable carcinoma of the breast is 10 to 40 mg. Because of
its short action, fluoxymesterone should be administered to patients in divided, rather than
single, daily doses to ensure more stable blood levels. In general, it appears necessary to
continue therapy for at least one month for a satisfactory subjective response, and for two to
three months for an objective response.
PRESENTATION
Halotestin 5 mg uncoated tablets, 100 tablets in the bottle
STORAGE
Store in a cool dry place between 15 – 25°C. Protect from direct light.